Prostate cancer has become the third most common cancer among men in Hong Kong, following lung and colorectal cancers. In recent years, the incidence has significantly increased, and there is a trend toward younger patients being diagnosed. Due to the diverse clinical presentations of prostate cancer, and the rapid growth of some cancer cells, over half of new patients are already at an advanced stage at the time of diagnosis, necessitating heightened awareness.
For early-stage prostate cancer diagnoses, doctors develop personalized treatment plans based on the patient’s age, overall health, cancer stage, and activity level. Common assessment tools include the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) index and the Gleason score. If the cancer's activity is low and the tumor is small, an active surveillance approach may be chosen. For patients with medium to high-risk cancer and larger tumor sizes, radical treatment options are recommended, such as local treatments or minimally invasive surgeries.
Local treatment options include High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU), cryotherapy, and the newer Irreversible Electroporation (IRE). The IRE procedure takes about an hour and does not rely on thermal or cryogenic methods; instead, it uses electrodes to release short pulses of high voltage and low current, inducing cancer cell apoptosis. This technique precisely targets tumors while avoiding damage to surrounding critical structures, like blood vessels and nerves, resulting in fewer side effects and faster recovery times.
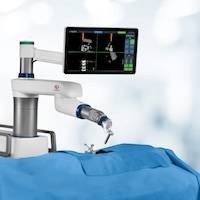
For patients at medium to high risk with larger tumors, minimally invasive surgery or radiation therapy (radiotherapy) can be considered. Minimally invasive surgery may be performed using robotic assistance, which helps in accurately removing the tumor and reconstructing the urethra while preserving surrounding prostate tissue, thus aiding in maintaining urinary and sexual function post-surgery. Radiation therapy uses high doses of X-rays to target the prostate and surrounding tissues, particularly suitable for patients who cannot undergo general anesthesia, have had multiple abdominal surgeries, or have other chronic health issues.
Currently, treatment options for prostate cancer are becoming increasingly diverse, with precision and effectiveness continuously improving. Patients should engage in discussions with their doctors to fully understand the pros and cons of each option and collaboratively develop the most suitable treatment strategy for their individual circumstances.