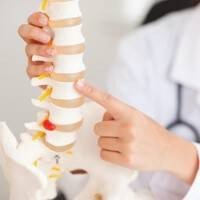
The most common symptom of a herniated disk is lower back pain. If lower back treatment does not alleviate the patient’s symptoms, and he/she also experiences symptoms of sciatica, the doctor may recommend an MRI to determine whether there is a tear or herniation in the spinal disk, and examine how this may be affecting the dural sac or nearby nervous tissues. As MRI technology does not involve the use of radiation, the diagnostic process is very safe.
Treatment
Most cases of disk herniation involve structural issues in the spine, such as chronic degeneration. If symptoms are not severe, or if the spinal canal is only slightly narrowed, the patient may only need adequate rest and appropriate exercise to manage the condition. The body may be able to secrete enzymes that naturally resolve the herniation, and patients may experience symptom relief within four to six weeks. Treatment of herniated disks generally focuses on pain relief, and may include medication, physical therapy, and surgery. In severe cases, surgery may be the only treatment option.
| Medication |
The doctor may prescribe pain medication and muscle relaxers to help relieve symptoms. If the patient is suffering from nerve-related pain, the doctor may prescribe neuropathic drugs. |
|
Physical Therapy
|
Specific exercises and positions may be recommended to help reduce inflammation and relax the muscles.
|
|
Surgery
|
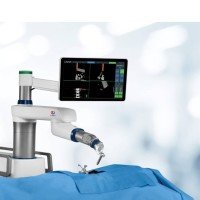
In severe cases where a nerve is compressed, the doctor may recommend minimally invasive surgery to release pressure on the spinal nerves. Patients generally recover quickly, but will need to avoid strenuous work or exercise and stretch regularly to maintain lower back health. In very severe cases where the spinal cord is displaced, spinal fusion or lumbar disk replacement surgery may be required.
|